Dedicated SMSC Simulator
The Dedicated SMSC Simulator (DSS) service provides customers with their own SMSC simulator that is accessible via SMPP for testing SMS-enabled applications. The simulator provides the means to test MO and MT SMS, and supports SMPP v3.3, v3.4 and v5.
SSH to DSS instance
The hostname and PEM will have been provided to enable you to SSH to your DSS.
SMSC Simulator instances run on AWS EC2 Linux instances.
ssh -I [file].pem ec2-user@[hostname]
where [file] and [hostname] represent the PEM file and instance hostname respectively.
tmux sessions
The DSS is installed as a service on EC2 instances launched from AWS Marketplace and does not run in tmux.
The DSS application, MLSMSCSimulator, should be run in a tmux session where not being run as a service. This allows the application to run without being connected to the host, and allows other applications to be run alongside, such as tshark for packet capturing.
To connect to an existing tmux session (where there is only one session):
tmux attach
To detach from the current tmux session:
Ctrl-B D
If there are multiple tmux sessions, then you can list them using:
tmux ls
To attach to a specific session:
tmux attach -t N (where N identifies the session)
SMSC Simulator application (MLSMSCSimulator or ec2MLSMSCSimulator)
The MLSMSCSimulator application is located in the home directory (/home/ec2-user) and can be run as follows:
./MLSMSCSimulator help
or
./ec2MLSMSCSimulator help
This will produce the following usage information:
SMSCSimulator (AWS_Marketplace_AMI) Melrose Labs - Build timestamp: Apr 17 2023 12:40:56
Usage: ./ec2MLSMSCSimulator [command] [options]
Commands:
run Run the SMSC Simulator on port 2775
gencredentials Generate a set of 5 SMPP credentials for connecting to this SMSC Simulator
help This help
version Print version information
Options:
--highiplimit Increases the max number of connections from a single IP address from 20 to 250
--dlrlatency Number of seconds between submission and DLR being generated (default 3s)
--guestmode Accept any SMPP credentials
--maxtps Maximum submit TPS allowed per bind
--port Port number to listen for SMPP connections
--ipwhitelist IP address to add to whitelist (DDoS protection)
Generate SMPP credentials
To generate SMPP credentials for applications to connect to the SMSC Simulator using SMPP, use the following command:
./MLSMSCSimulator gencredentials
or
./ec2MLSMSCSimulator gencredentials
The will produce output similar to the following:
$ ./MLSMSCSimulator gencredentials
./MLSMSCSimulator Melrose Labs - Build timestamp: Mar 2 2021 17:49:23
Generated SMPP Credentials (valid 90 days)
System ID Password
--------- --------
980632 30fc81
443358 32abd5
660692 45666f
905866 522c23
902174 c82cc4 The credentials will be valid for a limited amount of time (e.g. 90 days).
The SMPP system type is always null (empty).
If required, a system ID may be used simultaneously by multiple applications.
Starting the SMSC Simulator
AWS Marketplace instances (systemd service)
The DSS will automatically start when an AWS EC2 instance is launched or reboots.
To start DSS:
sudo systemctl start smscsimulator
To get the status of the DSS process:
sudo systemctl status smscsimulator
Running in tmux
Run the following:
./MLSMSCSimulator run
The following output should be seen:
$ ./MLSMSCSimulator run
./MLSMSCSimulator Melrose Labs - Build timestamp: Mar 2 2021 17:49:23
Starting SMSC Simulator
1614714406.253799 0x62d680 INFO SMPPServer::dolisten r=0 listensockfd=3
1614714406.253850 0x62d680 INFO SMPPServer::run Listening for SMPP on port 2775 (listensockfdSMPP=3) Stopping the SMSC Simulator
AWS Marketplace instances (systemd service)
To stop DSS:
sudo systemctl stop smscsimulator
Running in tmux
Sending a SIGINT/SIGTERM signal to the MLSMSCSimulator process will cause it to shutdown. One way of doing this is by typing Ctrl-C in the application’s session.
Routing of Mobile Originated SMS
By default, the destination address in a submit_sm can be used to route a message to the TRX or RX bind of a particular system ID. When doing this the system ID of the submitting application must be the same as the system ID of the receiving application, and so the submitter must only use a TX bind to ensure it does not have the message routed back to itself.
Source/destination address based routing
A routing configuration file (routing.config) can be used to route messages with source/destination addresses that start with specific digits delivered to binds of specific system IDs. The file should be located in the current working directory of the MLSMSCSimulator application.
When an application establishes an SMPP session with the SMSC Simulator, the routing configuration file is loaded for that session. Messages submitted with the submit_sm PDU are then processed using that loaded routing configuration file. Changes made to the routing configuration file will not take effect to an existing SMPP session.
The format of each line in the file is as follows:
Routing by source address
S:<prefix><SP><system-id>
Routing by destination address
D:<prefix><SP><system-id>
An example file is:
S:4400 294401
S:4410 614553In above example file would result in the following:
Messages with a source address starting 4400 would be routed to TRX and RX binds for system ID 294401
Messages with a source address starting 4410 would be routed to TRX and RX binds for system ID 614553
The routing configuration file can contain many entries.
Generating DLR status and errors
Where a dlr.conf is present, the default behaviour of generating “delivered” delivery receipts (DLRs) can be overridden. In the file, SMPP DLR status values are associated with a percentage value. This is used to generate DLRs of each status based on the stated percentages.
# DELIVERED (2)
2=85
# EXPIRED (3)
3=0
# DELETED (4)
4=0
# UNDELIVEABLE (5)
5=15
# ACCEPTED (6)
6=0
# UNKNOWN (7)
7=0
# REJECTED (8)
8=0CDR Files
Each SMPP submit_sm will result in a line in the cdr_T_N.log file, where T (YYYYMMDDHHMMSS) and N (epoch time) are when the SMSC Simulator application was started.
To avoid impacting performance, SMSC Simulator CDRs files are written when the SMSC Simulator is shutdown and when there is no activity.
Each line has the following format:
<ts>,<ts-epoch>,<system-id>,<srcaddr>,<destaddr>
Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
<ts-utc> | Timestamp (ISO8601)
|
|
<ts-epoch> | Timestamp (seconds to 6dp) | 1614723822.321123 |
<system-id> | System ID of the SMPP account submitting message | 123456 |
<srcaddr> | Source address of message | 4411000000 |
<destaddr> | Destination address of message | 4422000000 |
Transaction Logs
Transaction logs capture a conversation that is i) initiated with an inbound message into the SMSC Simulator that is then passed to an application, and ii) the resulting outbound message from the application to the SMSC Simulator.
Each SMPP submit_sm and deliver_sm will result in a line in the transaction_T_N.log file, where T (YYYYMMDDHHMMSS) and N (epoch time) are when the SMSC Simulator application was started.
SMSC Simulator transaction logs are written when the SMSC Simulator is shutdown.
Each line has the following format:
<S1-ts>,<S1-ts-epoch>,<S1-system-id>,<S1-srcaddr>,<S1-destaddr>,
<D1-ts>,<D1-ts-epoch>,<D1-system-id>,<D1-srcaddr>,<D1-destaddr>,
<S2-ts>,<S2-ts-epoch>,<S2-system-id>,<S2-srcaddr>,<S2-destaddr>
The S1 entries capture the inbound message into the SMSC Simulator.
The D1 entries capture the inbound message being passed to the application by the SMSC Simulator.
The S2 entries capture the outbound message from the application to the SMSC Simulator.
Destination address format
Acceptable destination addresses can be defined for each ESME system ID in a file of filename format esme_<systemid>.config.
shouldReturnUndeliveredReceipts is used to force all DLRs to return “undeliverable” status.
When a SubmitSM is made, if it does not conform to an allowedmsisdn, it will be rejected with an SMPP ESME_INVDSTADR command status error code.
{
"base": {
"return_undelivered_receipts": false
},
"allowedmsisdn": [
{
"CC": 91,
"Min": 9,
"Max": 12
},
{
"CC": 86,
"Min": 7,
"Max": 14
}
]
}Monitoring
Metrics are exposed by the DSS in the Prometheus text-based format. This format is supported in Prometheus version >=0.4.0.
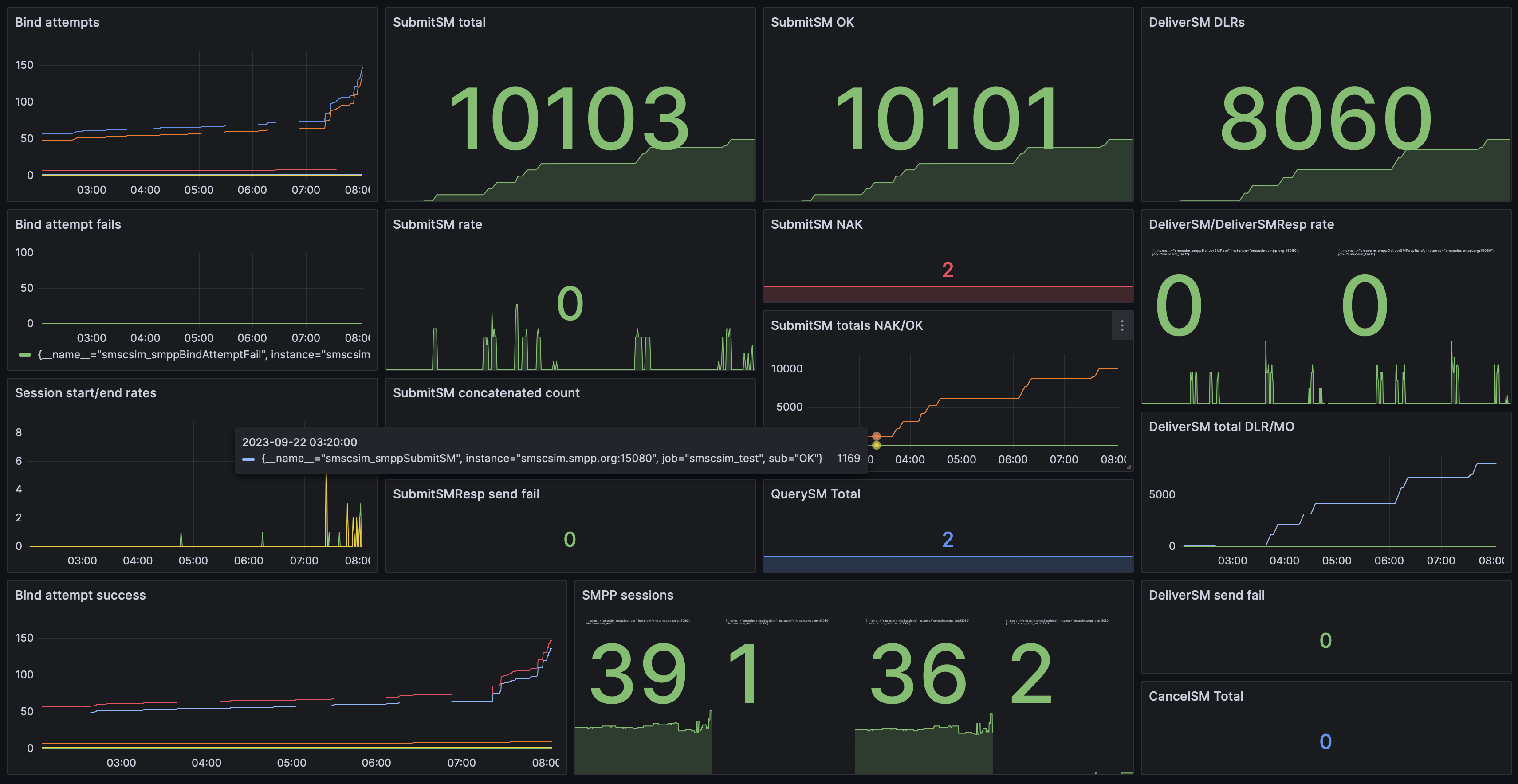
Dedicated SMSC Simulator dashboard in Prometheus/Grafana
Endpoint
GET /metricsNo credentials are required to access the metrics.
curl http://${DSSHOST}/metricsCommand-line options
Note: When using command-line options, the command “run” must be included to run the DSS.
Multiple options can be used on a command-line:
./MLSMSCSimulator run --maxtps 100 --dlrlatency 2Set maximum TPS for an SMPP bind (default 10000)
The following would set the maximum rate at which SMS can be submitted over a single SMPP bind to be 100 SMS:
--maxtps 100Accept any SMPP credentials
--guestmodeAllow more than 20 binds from a single IP address
--highiplimitWhitelist IP addresses
--ipwhitelist 1.1.1.1,2.2.2.2,3.3.3.3Set the DLR latency to 1s (default 3s)
--dlrlatency 1Set the DSM (DeliverSM) window to 50 (default 25)
--dsmwindow 50Set the final state retention period to 3600 secs (default 60 secs)
--finalstateretention 3600Set the port for SMPP connections to 9775 (default 2775)
--port 9775Set the port for HTTP connections to 8080 (default 12080)
Used for Prometheus metrics.
--httpport 8080