Operation
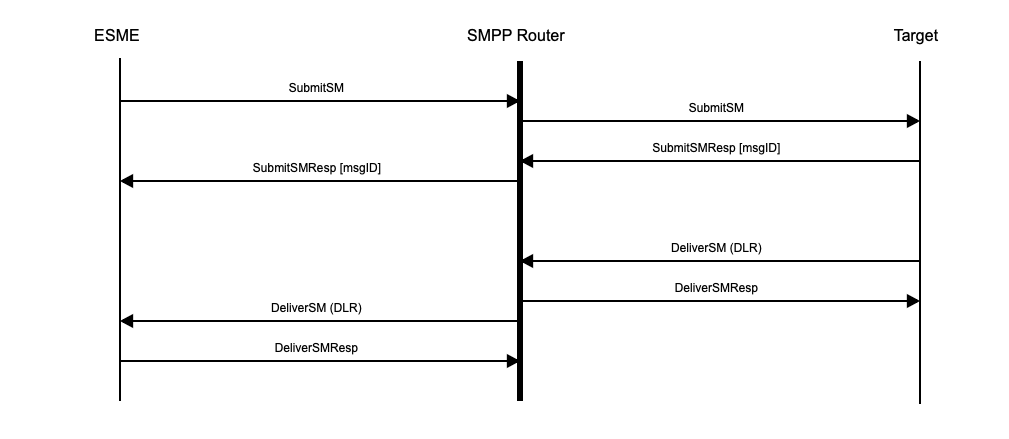
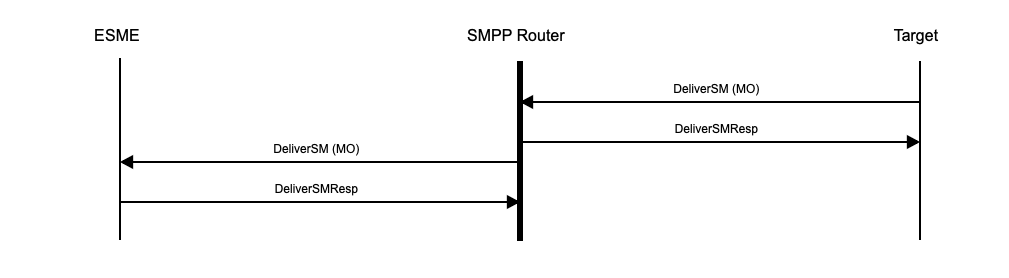
SMPP Router receives mobile terminated (MT) messages from ESME SMPP sessions and routes them to target SMPP sessions as shown in diagram 1. These target SMPP sessions are typically SMS gateway providers or MNO SMSC platforms. Similarly, it receives mobile originated (MO) messages from target SMPP sessions and routes them to ESME SMPP sessions as shown in diagram 2.
Messages from ESMEs can be routed to targets dedicated to the ESME (proxy traffic), or can be routed to targets that are shared by multiple ESMEs (multiplex traffic).
Diagram 1: SubmitSM from ESME to target for MT SMS and delivery receipt (DLR)
Diagram 2: MO SMS as DeliverSM from target to ESME
The routing of MT takes place to target sets, i.e. sets of targets. When routed to a target set, the traffic is load balanced over the targets in the target set based on the weights of each target. A target set can be specified in configuration for each ESME. If global or ESME-specific routing rules are defined, these will be used to affect which target set is used.
If an SMPP connection to a target is lost, SMPP Router will repeatedly attempt to reconnect to the target until successful.
Connections to targets can be set to “administratively down” by the administrator, resulting into the SMPP connection being brought down. In the case of a connection to a target being “administratively down”, no attempt will be made by SMPP Route to reconnect to the target until it is no longer “administratively down”. Setting/unsetting “administratively down” can be done in configuration, using the smpproutercli command-line too, or using the API.
Dynamic changes to configuration
Target SMSC connections are established when the SMPP Router is started or, when new targets are created while the SMPP Router is running. The bind quantity (bindqty), weight and UP/DOWN status (admindown) of a target SMSC can be modified using the API or command line without needing to restart SMPP Router.
ESME entries representing customers can be added, modified and removed while the SMPP Router is running without needing to restart.
Concatenated SMS
The SMPP Router tracks which upstream platform the first part of a concatenated SMS is routed to and routes each subsequent part via the same upstream platform.
The routing of parts takes into account the ESME SMPP session, mobile number and SAR reference to ensure there is no routing interference caused by different messages being sent to the same destination mobile.
The SMPP Router supports parts of a concatenated SMS being received out of order.
SMPP transactions
An SubmitSM PDU from an ESME is relayed by the SMPP Router to the target SMSC. The resulting SubmitSMResp PDU from the target SMSC is then relayed by SMPP Router to the ESME.
In the case of DeliverSM PDUs from a target SMSC, a DeliverSMResp is immediately sent by SMPP Router to the target SMSC before the DeliverSM is relayed to the ESME (see diagrams 1 and 2). On receipt of the DeliverSM, the ESME should generate a DeliverSMResp that is sent to SMPP Router but not relayed to the target SMSC as the DeliverSM has already been acknowledged to the target SMSC by SMPP Router.
Target sets
Target sets contain one or more SMSC connections (targets), and each target is intended to be dedicated to a single target set. The same target should not be defined in multiple target sets to avoid configuration conflicts or unintended behaviour.
MT routing
See the Routing section for further details on routing.
Single target-set mode
In this mode of operation, each ESME is associated with a single target set and therefore does not use multiple target sets. As a result, an ESME is restricted to using only the targets defined within its assigned target set.
This mode of operation is where an ESME’s traffic is routed over a single target set, irrespective of the destination mobile numbers. You accomplish this by:
using a
sharedtargetsetidto specify the target set that should be used by an ESME;do not use
routes-mtglobal or ESME-specific rules.
Multi target-set mode
In this mode, ESMEs can be associated with multiple target sets. This enables the selection of the most appropriate target set and target SMSC connection for each message.
You accomplish this by:
using a
sharedtargetsetidto specify the default target set that should be used by an ESME;use
routes-mtglobally and/or ESME-specific rule.
Message ID tracking (DLRs)
By default, SMPP Router tracks message IDs returned in SubmitSMResp PDUs to identify the ESME to where a subsequent DLR should be routed. Where each ESME has its own target set, DLR tracking can be disabled to reduce memory usage (see dlr.disable_msgid_tracking configuration parameter).